Hyperhidrosis, a condition characterized by sweating more than necessary to cool the body, often occurs without the usual causes, such as exercise or warm temperatures. Recognizing and effectively managing this condition is key, not only for identifying its signs and selecting the most appropriate treatment but also for minimizing its impact on your social interactions and confidence.
Understanding the Causes of Hyperhidrosis
Hyperhidrosis is categorized into two main types: primary and secondary.
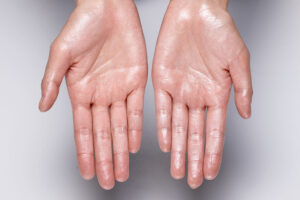
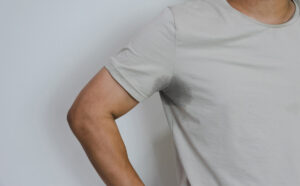
Primary hyperhidrosis stands as an independent condition, not linked to other health issues, and often targets specific regions like the palms, soles, underarms, or facial area. It’s thought to have a genetic component, suggesting a higher likelihood of occurrence if there’s a family history of such symptoms.
Conversely, secondary hyperhidrosis emerges as a consequence of different medical conditions or as a reaction to certain medications. It can be triggered by a range of health concerns, including but not limited to diabetes, thyroid disorders, infections, and issues within the nervous system. Medications prescribed for depression or hypertension are also known to potentially cause increased sweating.
While stress, anxiety, specific foods and beverages (notably caffeine and spicy items), and elevated temperatures can provoke hyperhidrosis in both its primary and secondary forms, it’s critical to understand that primary hyperhidrosis may manifest without any discernible triggers. [1]
Symptoms and Diagnosis
When it comes to navigating the complexities of hyperhidrosis, recognizing the symptoms and securing a proper diagnosis are crucial steps.
Identifying Hyperhidrosis Symptoms
In addition to the primary symptom of excessive sweating in specific areas, there are several other indicators to be aware of:
- Sweat that occurs on both sides of the body in a relatively symmetrical pattern is a hallmark of primary hyperhidrosis.
- Skin changes, such as softening, whitening, and, in severe cases, cracking, can occur in the areas that sweat excessively.
- Frequent skin infections, like athlete’s foot or jock itch, may be more common due to the moist environment created by excessive sweating.
- Disruption of daily activities, where even simple tasks become difficult; for instance, turning a doorknob, using a computer, or holding a pen can be challenging due to slippery hands.
- Cold and clammy hands and feet, even in warm conditions, due to persistent sweating.
- Increased sweating during periods of stress, which can exacerbate the condition and create a cycle of anxiety and sweating.
These symptoms can vary in intensity and may not all be present in every individual with hyperhidrosis. The degree to which hyperhidrosis affects your daily life and well-being can also fluctuate. [2]
How to Get a Diagnosis: Steps and Tests
Securing a diagnosis for hyperhidrosis involves a detailed evaluation by your healthcare provider. Start by documenting your symptoms, noting when and where you sweat most, and how it affects your daily activities. Your doctor may conduct a physical examination and review your medical history to rule out underlying conditions that could be causing your symptoms.
Specific tests, like the starch-iodine test, can be applied to the sweaty area; it turns dark blue where there’s excessive sweat. Another diagnostic tool is the thermoregulatory sweat test, which uses a special powder that changes color in areas where you sweat excessively. In some cases, blood tests might be ordered to exclude other medical conditions, like hyperthyroidism or diabetes, that can cause similar symptoms. [3]
Comprehensive Treatment Options
Embarking on the journey to manage hyperhidrosis involves exploring a variety of treatment options.
Medical Treatments
Medical treatments for hyperhidrosis offer a range of options designed to target excessive sweating at its source. Each of these treatments has its own specific application and effectiveness, depending on the severity and location of your hyperhidrosis.
- Antiperspirants containing aluminum chloride hexahydrate are a first-line treatment, working by temporarily blocking sweat ducts.
- Medications, such as anticholinergics, can reduce sweating by inhibiting certain nerve signals, although they may come with side effects like dry mouth and blurred vision.
- Iontophoresis involves using a device that passes a mild electrical current through water and into the skin’s surface, effectively reducing sweat production in treated areas.
- Botox injections temporarily block the nerves that trigger sweat glands. [4]
Surgical Options: Endoscopic Thoracic Sympathectomy (ETS)
For severe cases of hyperhidrosis that do not respond to other treatments, ETS may be considered. This surgical procedure involves interrupting the sympathetic nerves responsible for excessive sweating, particularly in the palms and underarms.
While ETS can be highly effective, it’s important to be aware of the potential for compensatory sweating in other areas of the body, a side effect where sweating increases elsewhere to compensate for the reduction in the treated area. [5]
Alternative and Natural Remedies
In addition to medical and surgical treatments, there are alternative and natural remedies that some individuals find helpful in managing hyperhidrosis. These can include herbal supplements, acupuncture, yoga, and dietary changes aimed at reducing sweat triggers. While the scientific evidence supporting the effectiveness of these methods varies, they may offer complementary benefits alongside more conventional treatments. [6] [7]
Lifestyle Changes and Management Strategies
Adopting specific lifestyle changes and management strategies can play a pivotal role in improving your quality of life.
Daily Routines and Wardrobe Choices
Opt for clothing made from natural, breathable fabrics like cotton, bamboo, and linen, which allow better air circulation and can absorb sweat more effectively than synthetic materials. Light colors and loose-fitting garments can also help conceal sweat marks and provide comfort. Incorporating sweat pads or liners into your clothing can offer an additional layer of protection against sweat stains. Choosing the right footwear and changing socks throughout the day can also alleviate discomfort, especially for those with plantar hyperhidrosis. [8]
Diet and Exercise Implications
Certain foods and beverages, such as spicy dishes, caffeine, and alcohol, may trigger sweating. Observing how your body reacts to different foods can guide you in making dietary choices that may help reduce symptoms. Staying hydrated is essential, as it can help regulate body temperature. [9]
Regular exercise, while it naturally increases sweating, is beneficial for overall health and stress reduction. However, choosing the right time to exercise and selecting activities that allow you to manage sweating comfortably is key. [10]
Integrating these lifestyle changes and management strategies into your daily life requires commitment and experimentation to find what works best for you. Remember, managing hyperhidrosis is a personal journey.
Discover how SweatBlock, the leading clinical-strength antiperspirant sold online, can help you regain confidence and control over your embarrassing sweat problems today.
About the Author
Dr. Ali is a medical journalist and copywriter.
You might also like...

Why Does My Face Sweat So Much?: Tips And Treatments For Face Sweating
Table of Contents Do you ever feel like you’re the sweatiest person in the room?

How to Stop Sweating Naturally – Huge List Tips & Home Remedies
Table of Contents For most people, sweating is a totally natural bodily function. For others,

Top 10 Best Deodorants For Sweaty Armpits
Do you struggle with sweaty armpits? Has your deodorant let you down when it comes